Author’s Note: This blog was originally published in October 2021 and has been updated to be fresh, accurate, and comprehensive.
A Note on This 2025 Update
When we first published this guide in October 2021, the world was still emerging from pandemic disruption. Businesses were scrambling to digitize operations, and RPA was primarily seen as a cost-cutting emergency measure—a way to do more with fewer people in the office.
Four years later, the landscape has completely transformed.
RPA is no longer just about survival or cost reduction. In 2025, it’s a strategic capability that separates market leaders from those struggling to keep pace. What began as simple task automation has evolved into intelligent process orchestration, where RPA integrates seamlessly with AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics to handle increasingly complex workflows.
The numbers tell the story: The global RPA market was valued at USD 3.79 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $43.5 billion by 2030—a CAGR of 43.9%. But more importantly, how businesses use RPA has fundamentally changed. Companies that started with basic data entry automation in 2021 are now running hundreds of interconnected bots managing end-to-end business processes.
This updated guide reflects that evolution. We’ve revised every section based on insights from implementations we’ve completed, and included real-world outcomes we’ve witnessed as RPA has matured.
If you’re exploring RPA in 2025, you’re entering at the right time—the technology is proven, the tools are sophisticated, and the implementation playbooks are battle-tested.
The Current State of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Companies
Do you run a manufacturing company, operate in supply chain or logistics, manage a healthcare organization, or oversee financial operations? No matter what industry your business belongs to, Robotic Process Automation has evolved from a “nice to have” into a competitive necessity.
When the pandemic hit in 2020, it affected not only our health but also the health of businesses worldwide. Leaders were forced to focus on cost reduction, business continuity, and maintaining customer satisfaction with distributed teams. RPA emerged as one of the few technologies that could address all three simultaneously—and that initial momentum has only accelerated.
Here’s what changed between 2021 and now:
Then (2021): Companies adopted RPA reactively—to handle remote work challenges, maintain operations with reduced staff, and survive economic uncertainty.
Now (2025): Companies deploy RPA strategically—to scale without proportional cost increases, integrate disparate systems faster than traditional IT approaches, and create operational capabilities competitors can’t easily replicate.
Looking ahead (2026+): RPA is converging with AI, enabling bots that don’t just follow rules but understand context, make intelligent decisions, and continuously optimize their own performance. The combination of RPA’s reliability with AI’s adaptability is creating automation capabilities that seemed like science fiction just a few years ago.
This guide will help you understand RPA as it exists today: its benefits and features, when it makes sense for your company (and when it doesn’t), and how to implement it successfully based on what we’ve learned from hundreds of deployments.
📖 Further Reading
Looking for the right RPA platform?
Check out our comprehensive guide:
10 Best RPA Tools and Their Features in 2025
– comparing features, pricing, and ideal use cases for UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism, and more.
Want to avoid common pitfalls?
Read our analysis:
5 Major Challenges to Consider Before Implementing RPA
– based on real obstacles our clients have faced and solved.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Definition of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is an automation technology that mimics human actions performed on a computer. It can interact with systems in ways similar to humans, such as using the keyboard, moving the mouse, and reading data from the screen.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is software technology that mimics human actions within digital systems. Just like humans, RPA interacts with various computer applications and performs assigned tasks without requiring human intervention.
What makes RPA unique is how it works: it doesn’t require API integrations or system modifications. Instead, RPA bots interact with your existing software the same way humans do—typing on keyboards, clicking mice, reading data from screens, and moving information between applications. This approach means RPA can work with any system that has a user interface, including legacy systems built decades ago.
RPA can execute a wide range of activities, from simple tasks like data entry to more complex processes that involve decision-making based on predefined rules. For example, an RPA bot can extract invoice data, validate it against purchase orders, enter it into your ERP system, and flag exceptions for human review—all without changing your existing software.
Using RPA for business process automation significantly speeds up workflows and reduces operational costs. Organizations can complete tasks more efficiently without sacrificing quality or accuracy. In our experience across manufacturing, healthcare, and financial services, RPA typically reduces process time by 60-80% while virtually eliminating manual errors.
Additionally, RPA is designed to work seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure. You don’t need to overhaul systems or wait for lengthy integration projects. Most RPA implementations go live within 4-8 weeks, compared to 6-18 months for traditional system integrations.
Now that we’ve established what RPA is, let’s examine its key features and how they translate into business value.
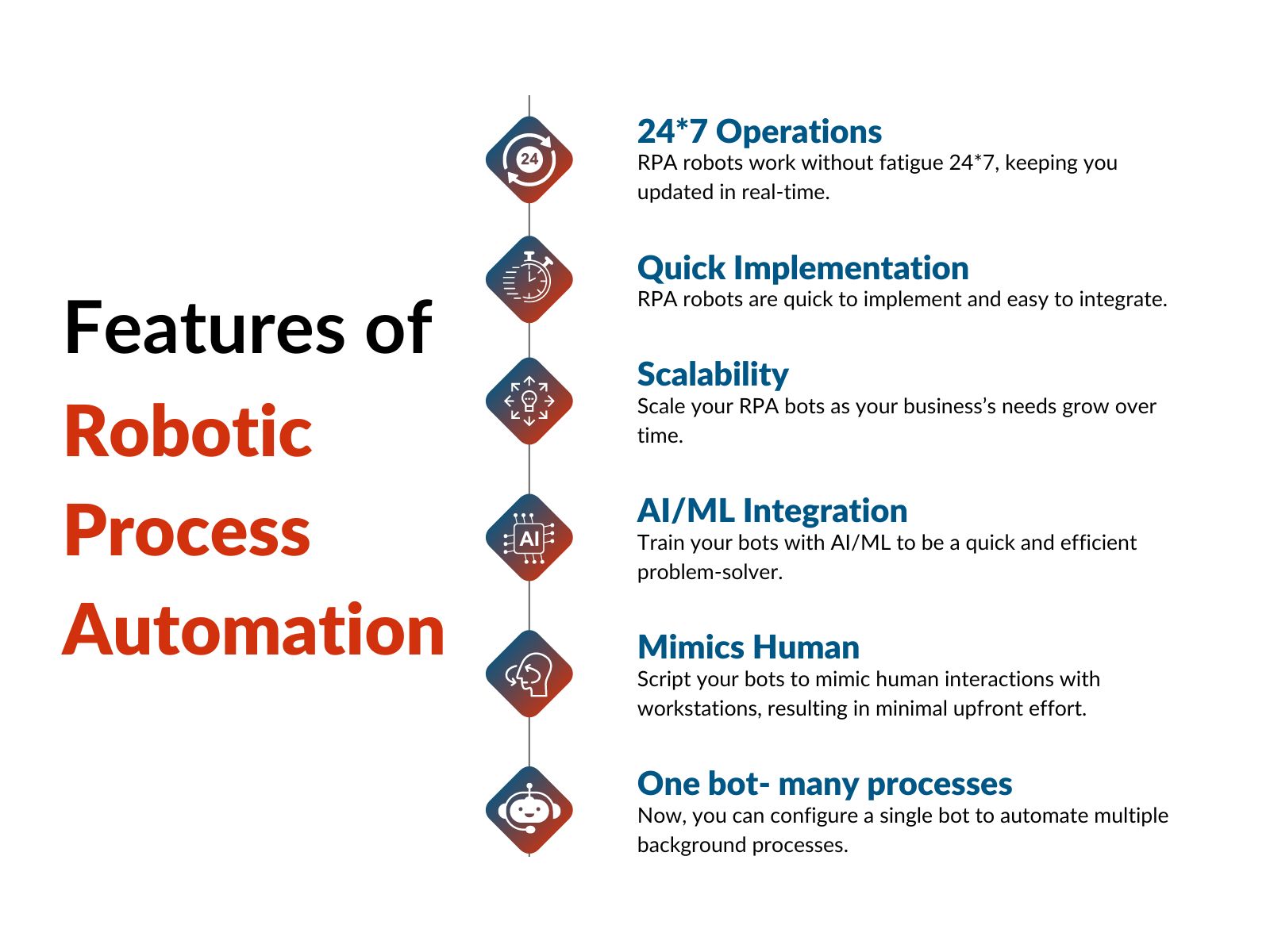
Features of Robotic Process Automation
RPA platforms offer several distinctive features that make them effective for business automation. Here are seven significant capabilities that set RPA apart:
Features of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- 24×7 Operations
- Quick Implementation
- Scalability
- AI/ML Integration
- Mimics Human
- Multi-application Orchestration
24×7 Operations
Unlike human workers, RPA bots don’t need breaks, sleep, or time off. They can work continuously around the clock, processing transactions overnight or during weekends when your team isn’t available. This means tasks that would take your team multiple business days can complete overnight. You receive real-time updates and alerts for any deviations anytime, anywhere, ensuring continuous monitoring without constant human supervision.
Real-world impact: Organizations process updates and transactions 24/7, ensuring customers and stakeholders receive information immediately rather than waiting until the next business day.
Quick Implementation
Most RPA solutions can be developed and deployed within 4-8 weeks for standard processes. This rapid implementation cycle means you start seeing ROI within months, not years. RPA bots are designed to integrate easily with your existing systems without requiring extensive IT infrastructure changes, making them powerful enough to scale as your requirements grow.
Implementation reality: Simple single-system processes take 2-3 weeks; complex multi-system workflows take 6-8 weeks from assessment to deployment.
Flexibility and Scalability
As your business requirements change, you can quickly increase or decrease the number of bots. Need to handle a seasonal surge in orders? Deploy additional bots in days. Volume returning to normal? Scale back without the complications of hiring and layoffs. RPA bots are quick to develop, modify, and deploy, giving you operational agility that’s impossible with manual teams alone.
Strategic advantage: Companies handle significant volume increases without proportionally increasing headcount, making growth more profitable.
AI and ML Integration
Modern RPA platforms integrate seamlessly with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities. While basic RPA follows rules, adding AI allows bots to handle unstructured data, make intelligent decisions, and continuously improve. This combination expands RPA’s capabilities from structured, predictable processes to scenarios requiring intelligence and adaptability.
When this matters: Processes involving unstructured documents, emails, or scenarios requiring pattern recognition benefit significantly from combining RPA with AI. For instance, when processing invoices with varying formats, AI handles the intelligent data extraction while RPA manages the workflow.
Mimics Human Actions
RPA bots replicate how humans interact with computer systems—they log in, navigate applications, read data, make entries, and move information between systems. This capability means you can automate systems that lack APIs or modern integration options. Legacy systems that “should have been replaced years ago” suddenly become automation candidates.
Why this is powerful: Many organizations run critical operations on decades-old systems that work perfectly well but can’t easily integrate with modern applications. RPA bridges that gap.
Multi-Application Orchestration
RPA bots seamlessly work across multiple applications simultaneously—ERP systems, web applications, desktop software, databases, and documents—without getting confused or losing context. A single bot can extract data from emails, validate it in your CRM, enter it into your ERP, and generate a confirmation document, all as one continuous workflow.
Operational benefit: Eliminates the “swivel chair” problem where employees copy data between systems, reducing errors and saving enormous amounts of time.
When to Implement RPA Makes (and When Not to)
Not every process should be automated with RPA. Based on hundreds of implementations, here’s a practical framework for determining if RPA is right for your situation:
Choose RPA When
Your process is high-volume and repetitive
If a task is performed dozens or hundreds of times daily following the same basic pattern, it’s likely a strong RPA candidate. Examples include invoice processing, order entry, claims handling, and report generation. The higher the volume, the greater the potential ROI from automation.
You’re working with legacy systems
When your critical systems lack APIs and integration would require expensive custom development, RPA offers a faster, lower-risk alternative.
You need fast results
Traditional system integration projects take 6-18 months. RPA delivers working automation in 4-8 weeks, making it ideal when speed matters.
Accuracy and compliance are critical
RPA bots create automatic audit trails for every action, making them excellent for regulated industries where documentation is mandatory.
Consider Alternatives When
Your process requires genuine judgment
If tasks involve subjective decision-making, interpreting nuanced context, or creative problem-solving, RPA alone isn’t sufficient. You’ll need AI capabilities or human expertise.
You’re dealing with highly unstructured data
While AI-enhanced RPA can handle some variability, processes involving completely unstructured inputs may need different solutions.
Your process changes frequently
If business rules change monthly, constant bot reconfiguration becomes costly. RPA works best for stable processes.
Your volume is too low
If a process only takes 10-20 hours monthly, automation may not provide sufficient ROI to justify the investment.
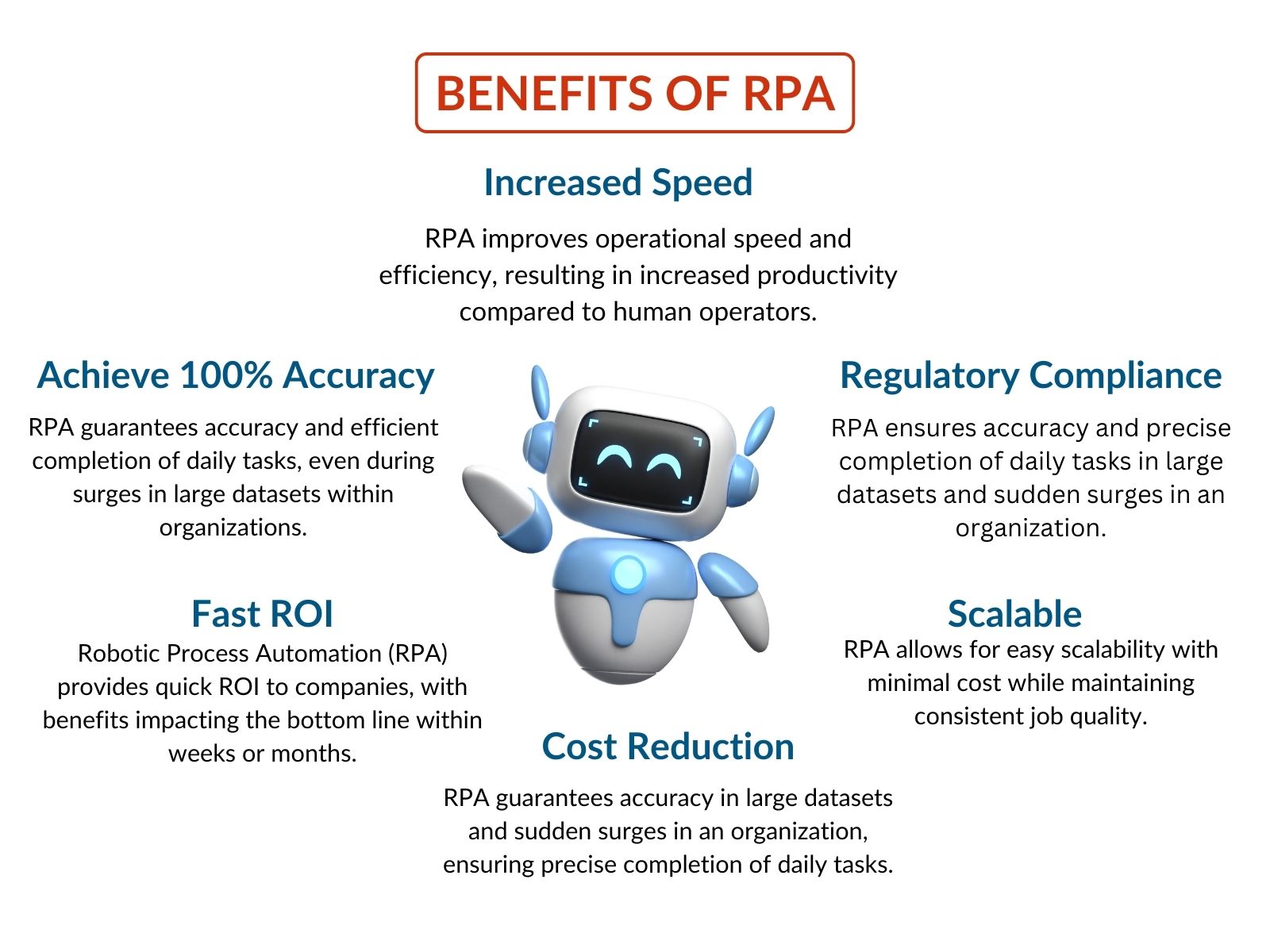
Benefits of Robotic Process Automation
Now that you understand RPA’s features and when it makes sense, let’s examine the concrete benefits your company can expect. Based on our implementation data, here are the six most impactful advantages:
Benefits of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- Achieve 100% Accuracy
- Increased Speed
- Regulatory Compliance
- Cost Reduction
- Scalable
- Fast ROI
Achieve Near-Perfect Accuracy
RPA dramatically improves accuracy in daily operations. While humans typically maintain 95-98% accuracy on repetitive data entry tasks (and lower when fatigued), RPA bots consistently deliver 99.5%+ accuracy regardless of data volume or time of day. Whether processing thousands of invoices or handling an unprecedented spike in transactions, bots maintain the same precision.
Measured impact: Organizations implementing RPA see error rates drop from typical manual levels (2-5% errors) to near-zero (0.1-0.5% errors). This dramatic reduction virtually eliminates costly mistakes that previously required correction and caused downstream problems.
Increased Processing Speed
Bots process transactions significantly faster than manual handling. They don’t need to look up information, switch between applications, or pause to think—they execute at computer speed. This leads to smoother operations, higher throughput, and improved productivity.
Measured impact: Average processing time reduction of 60-80% across implementations. A task taking 10 minutes manually completes in 2-3 minutes or even a few seconds with RPA, depending on the process complexity and systems involved.
Enhanced Regulatory Compliance
RPA bots follow predefined processes exactly every single time, ensuring consistent compliance with regulations and internal controls. The unique and secure login credentials provide complete transparency into who did what and when. Every action is automatically logged with timestamps and data values, creating audit trails that would be nearly impossible to maintain manually.
Why this matters: During regulatory audits, organizations can produce complete documentation instantly instead of spending weeks compiling manual records. This dramatically reduces audit preparation time and ensures compliance confidence.
Significant Cost Reduction
The combination of speed and accuracy leads to substantial cost savings. Bots handle more volume in less time with fewer errors, optimizing resource utilization and dramatically reducing the cost per transaction.
Measured impact: According to industry reports, a small company spends an average of $15 on processing a single invoice manually. For larger enterprises, expenses can reach as much as $40 per invoice. Based on these figures, the annual cost of processing 30,000 invoices for small enterprises is $450,000. For large companies at $40 per invoice, the cost reaches $1,200,000 annually.
Through invoice automation with RPA, the cost drops to approximately $1 per invoice. These considerable savings on invoice processing help businesses become significantly more profitable while handling the same or greater volumes.
Rapid Scalability
When business grows, RPA scales immediately. The robotic workforce can increase or decrease with minimal cost and zero compromise on quality. Compare this to hiring and training new employees, which takes months and involves significant risk.
Strategic value: Companies handle seasonal peaks, unexpected growth, or market expansion without the lag time of traditional scaling. Organizations can manage significant volume increases with the same team size after RPA implementation, making growth more profitable.
Fast Return on Investment (ROI)
RPA delivers ROI faster than most automation approaches. While traditional system integration projects may take years to recoup investment, RPA typically begins showing returns within months of deployment.
Financial reality: High-volume processes often break even quickly, with some implementations recovering costs within 3-6 months. The ongoing benefits accumulate year after year as the same bots continue processing transactions without additional labour costs, making the long-term ROI extremely compelling.
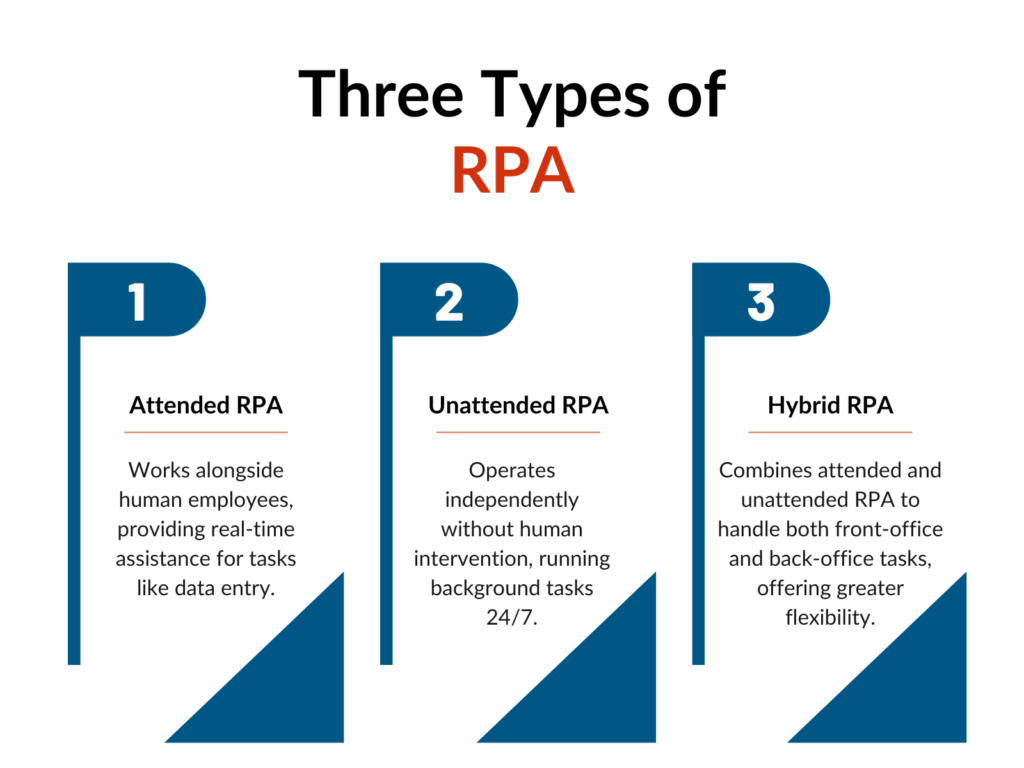
Types of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
There are three main types of Robotic Process Automation (RPA): attended automation, unattended automation, and hybrid RPA. Each type serves different operational needs within a business.
Let’s look at each type closely.
Types of RPA:
- Attended RPA: Works with human employees, helping them in real time with tasks.
- Unattended RPA: Operates independently without human help, handling background tasks 24/7.
- Hybrid RPA: Combines both attended and unattended RPA, managing tasks in both the front-office and back-office for more flexibility.
1. Attended RPA
Attended RPA is designed to work alongside human employees, assisting them with daily tasks and operations.
These intelligent bots are activated by user actions, providing immediate, real-time help by automating repetitive tasks like data entry, customer service interactions, and other routine activities. They are especially useful in front-office operations, where humans still need to handle complex tasks that can’t be fully automated due to their complexity.
For example, in a customer service setting, an attended RPA bot can quickly gather relevant customer information from various databases, speeding up the resolution process. This improves service efficiency, reduces wait times, and ensures quicker, more accurate resolutions, which boosts overall customer satisfaction.
Additionally, these bots can multitask, freeing up human employees to focus on more strategic, high-value work, resulting in a more productive and satisfied workforce.
2. Unattended RPA
Unattended RPA operates independently without any human input. These advanced bots run continuously, 24/7, in the background of an organization’s systems.
They handle a range of predefined tasks, such as complex data processing and batch operations, ensuring that crucial backend processes continue without interruption. These bots are perfect for high-volume tasks with minimal decision-making requirements, making them highly efficient. They can be scheduled or triggered by specific conditions, ensuring the timely execution of essential operations.
Unattended RPA is particularly useful in back-office operations where efficiency and cost savings are key. For instance, an unattended RPA bot can manage payroll processing, ensuring that all employees are paid accurately and on time without human oversight.
This reduces human error and frees up employees to focus on more valuable, strategic tasks. Essentially, unattended RPA helps businesses streamline operations and improve productivity.
3. Hybrid RPA
Hybrid RPA combines the capabilities of both attended and unattended RPA to offer a more flexible and comprehensive automation solution. This approach allows seamless collaboration between human workers and bots, integrating both front-office and back-office tasks. With hybrid RPA, organizations can manage end-to-end processes that require both attended and unattended tasks, offering greater flexibility and scalability for complex workflows.
Hybrid RPA benefits organizations by optimizing operations from start to finish. It enhances efficiency and accuracy across processes. For example, in the employee onboarding process, hybrid RPA can automate data entry tasks like collecting personal information and setting up profiles while also providing real-time support to HR staff for more complex tasks such as conducting interviews and managing sensitive documents.
Additionally, hybrid RPA can be tailored to various industries and use cases, making it a versatile tool to improve performance. In finance, for instance, it can automate routine transactions while allowing employees to focus on strategic tasks. In healthcare, it can manage patient records and appointment scheduling, giving medical professionals more time for patient care.
Industry-Wise RPA Use Cases
RPA delivers value across industries, but implementation approaches vary based on sector-specific needs. Here are the industries where RPA creates the most significant impact:
Manufacturing
High-impact applications include purchase order processing, supplier invoice reconciliation, production scheduling coordination, inventory monitoring, and quality control documentation. Manufacturers particularly benefit from RPA’s error elimination—when the wrong parts get ordered due to data entry mistakes, production stops. RPA prevents these costly disruptions.
Explore RPA use cases in Manufacturing →
Healthcare
Critical use cases include patient registration, insurance verification, claims processing, appointment scheduling, and medical billing. Healthcare organizations value RPA’s perfect audit trails and compliance documentation, which are essential in heavily regulated environments.
Discover Automation opportunities in Healthcare →
Finance
Key applications include loan processing, account reconciliation, regulatory reporting, compliance documentation, and period-close processes. Financial institutions particularly appreciate RPA’s automatic logging of every action, making audit preparation dramatically easier.
Learn about Finance Automation solutions →
Insurance
Primary uses include claims intake and assessment, policy administration, underwriting data collection, fraud detection support, and customer onboarding. Insurance companies benefit from RPA’s ability to handle high volumes while maintaining perfect compliance documentation.
Explore RPA in Insurance industry →
Education
RPA streamlines student admissions, enrolment processing, attendance tracking, grade management, and administrative reporting. Educational institutions use automation to reduce administrative burden and allow staff to focus on student support.
See RPA applications in Education sector →
Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector uses RPA for asset monitoring data processing, regulatory compliance reporting, energy production tracking, and maintenance scheduling. Automation helps manage the complex data flows inherent in renewable energy operations.
Summing Up
Robotic Process Automation has come a long way since its early days. What began in 2016-2018 as simple screen-scraping technology evolved into enterprise-grade automation by 2021, and in 2025, it’s becoming the foundation for intelligent, AI-powered business operations.
The explosive market growth—from $3.79 billion in 2024 to a projected $43.5 billion by 2030—isn’t just about more companies adopting the same technology. It’s about RPA evolving into something more sophisticated: an orchestration layer that connects people, systems, data, and AI into seamless, efficient workflows.
Business leaders worldwide are implementing RPA rapidly because it delivers measurable benefits—improved accuracy, increased speed, reduced costs, better compliance, and rapid scalability. But more importantly, it’s creating strategic advantages that compound over time as bots multiply, learn, and optimize.
However, RPA isn’t a universal solution. The key to success is understanding when it’s the right tool for your specific situation. High-volume, repetitive, rule-based processes with clear business value remain ideal candidates. Processes requiring creativity, judgment, or handling of highly unstructured data need AI augmentation or different approaches entirely.
If you operate in manufacturing, healthcare, finance, logistics, or similar industries with significant manual processing, RPA likely has a place in your automation strategy. The question isn’t whether to automate—it’s which processes to automate first, how to implement effectively, and how to build capabilities that scale with your business.
The companies thriving in 2025 aren’t asking “Should we adopt RPA?” They’re asking “How fast can we scale our automation capabilities?” That’s the mindset shift from 2021 to now.
Spread and share these benefits and features of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) within your organization.
Choose RPATech for unmatched RPA services
RPATech is a globally leading RPA Service provider, providing RPA Services and Solutions across manufacturing, healthcare, financial services, and other industries.
If you’re looking to implement RPA and want expert consultation to determine the right approach for your business, we’re here to help. Our team can assess your processes, provide honest guidance on automation feasibility, and design solutions tailored to your specific requirements.
Book a free consultation here
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
RPA generally does not require extensive coding skills. Most modern RPA platforms offer user-friendly, visual interfaces that allow business analysts to build bots using drag-and-drop functionality. However, for complex scenarios involving custom logic or integrations, some programming knowledge can be beneficial.
RPA mimics human actions to interact with software applications through user interfaces, while API integration allows direct system-to-system communication. RPA is typically used when APIs don’t exist (legacy systems) or when the integration needs to span multiple disconnected applications. APIs are preferred when available and when building long-term, high-volume integrations between modern systems.
Workflow automation orchestrates and routes tasks between people and systems, defining who does what and when. RPA executes the actual repetitive tasks within applications—like data entry, extraction, and processing. Think of workflow automation as the process manager and RPA as the worker performing manual tasks. Many organizations use both together: workflow automation manages the process flow while RPA handles the repetitive execution work.
- Attended RPA: Works alongside human employees, providing real-time assistance for tasks like data entry.
- Unattended RPA: Operates independently without human intervention, running background tasks 24/7.
- Hybrid RPA: Combines attended and unattended RPA to handle both front-office and back-office tasks, offering greater flexibility.
AI and RPA serve different purposes. RPA is best for automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, while AI excels at handling tasks that require learning, decision-making, and pattern recognition. Combining both can offer a powerful solution for complex automation needs.
Yes, this is one of RPA’s greatest strengths. RPA can interact with any system that has a user interface, regardless of age. If a human can use the system, a bot can too. We’ve successfully automated processes on systems from the 1990s that lack APIs and modern integration capabilities. RPA doesn’t require changes to the legacy system itself—it simply mimics how users interact with it.
RPA can interact with legacy systems without requiring changes to the underlying code or infrastructure. It mimics user actions to perform tasks, making it an effective solution for integrating and automating processes across outdated systems that lack modern APIs.
ROI timelines vary significantly based on process volume and complexity. High-volume processes with thousands of monthly transactions typically show returns faster than lower-volume processes. The payback period also depends on factors like current manual processing costs, error rates, and the complexity of automation required. Most organizations begin seeing measurable cost savings within the first few months after deployment, with returns accelerating as the automation stabilizes and scales.
Absolutely. RPA and AI are complementary, not competitive. While AI excels at understanding unstructured data and making intelligent decisions, RPA remains the most efficient way to automate structured, repetitive processes and orchestrate workflows across multiple systems. The trend is actually toward combining them—using RPA for process automation and reliability while leveraging AI for intelligence and handling variability. This hybrid approach delivers capabilities neither technology provides alone.